| Bigfoot | |||
|---|---|---|---|

| |||
| Naming | |||
| Others | Sasquatch | ||
| Binomen | N/A | ||
| Morphology | |||
| Body type | Humanoid | ||
| Average height | ~ 2 - 2.5 meters | ||
| Average weight | ~ 200kg | ||
| Intelligence | |||
| Sapience | Generally regarded as semi-sapient | ||
| Aggressivity | Variable | ||
| Ecology | |||
| Place of origin | Northwestern North America | ||
| Habitat | Woodlands | ||
| Diet | Omnivorous | ||
| Locomotion | Bipedal | ||
| Lifespan | Unknown | ||
| Related species | Dustman, Grassman, Skunk Ape, Yeti, Yowie | ||
| Status | DD | ||
| Behind the Scenes | |||
| Universe | Real | ||
Bigfoot, also known as Sasquatch, is purportedly an ape-like creature that inhabits forests, mainly in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Bigfoot is usually described as a large, hairy, bipedal humanoid. The term "sasquatch" is an anglicized derivative of the word "Sésquac" which means "wild man" in a Salish Native American language.
A majority of scientists discount the existence of Bigfoot and consider it to be a combination of folklore, misidentification, and hoax, rather than a legitimate animal, in part because some estimate large numbers necessary to maintain a breeding population. A small minority of accredited researchers such as Jane Goodall and Jeffrey Meldrum have expressed interest and possible belief in the creature, with Meldrum expressing the opinion that evidence collected of alleged Bigfoot encounters warrants further evaluation and testing. Nevertheless, Bigfoot remains one of the more famous and controversial examples of a cryptid within cryptozoology and an enduring legend. There are several regional Bigfoots.
Description
Bigfoot is described in reports as a large hairy ape-like creature, ranging between 6–10 feet (2–3 m) tall, weighing in excess of 500 pounds (230 kg), and covered in dark brown or dark reddish hair. Alleged witnesses have described large eyes, a pronounced brow ridge, and a large, low-set forehead; the top of the head has been described as rounded and crested, similar to the sagittal crest of the male gorilla. Bigfoot is commonly reported to have a strong, unpleasant smell by those who claim to have encountered it. The enormous footprints for which it is named have been as large as 24 inches (60 cm) long and 8 inches (20 cm) wide. While most casts have five toes—like all known apes—some casts of alleged Bigfoot tracks have had numbers ranging from two to six. Some have also contained claw marks, making it likely that a portion came from known animals such as bears, which have five toes and claws. Some proponents have also claimed that Bigfoot is omnivorous and mainly nocturnal.
History
Before 1958
Wildmen stories are found among the indigenous population of the Pacific Northwest. The legends existed prior to a single name for the creature. They differed in their details both regionally and between families in the same community. Similar stories of wildmen are found on every continent except Antarctica. Ecologist Robert Michael Pyle argues that most cultures have human-like giants in their folk history: "We have this need for some larger-than-life creature."
Members of the Lummi tell tales about Ts'emekwes, the local version of Bigfoot. The stories are similar to each other in terms of the general descriptions of Ts'emekwes, but details about the creature's diet and activities differed between the stories of different families.
Some regional versions contained more nefarious creatures. The stiyaha or kwi-kwiyai were a nocturnal race that children were told not to say the names of lest the monsters hear and come to carry off a person—sometimes to be killed. In 1847, Paul Kane reported stories by the native people about skoocooms: a race of cannibalistic wild men living on the peak of Mount St. Helens. The skoocooms appear to have been regarded as supernatural, rather than natural.
Less menacing versions such as the one recorded by Reverend Elkanah Walker exist. In 1840, Walker, a Protestant missionary, recorded stories of giants among the Native Americans living in Spokane, Washington. The Indians claimed that these giants lived on and around the peaks of nearby mountains and stole salmon from the fishermen's nets.
The local legends were combined together by J. W. Burns in a series of Canadian newspaper articles in the 1920s. Each language had its own name for the local version. Many names meant something along the lines of "wild man" or "hairy man" although other names described common actions it was said to perform (e.g. eating clams). Burns coined the term Sasquatch, which is from the Halkomelem sásq’ets (IPA: [ˈsæsqʼəts]), and used it in his articles to describe a hypothetical single type of creature reflected in these various stories. Burns's articles popularized both the legend and its new name, making it well known in western Canada before it gained popularity in the United States.
After 1958
In 1951, Eric Shipton had photographed what he described as a Yeti footprint. This photograph generated considerable attention and the story of the Yeti entered into popular consciousness. The notoriety of ape-men grew over the decade, culminating in 1958 when large footprints were found in Del Norte County, California, by bulldozer operator Gerald Crew. Sets of large tracks appeared multiple times around a road-construction site in Bluff Creek. After not being taken seriously about what he was seeing, Crew brought in his friend, Bob Titmus, to cast the prints in plaster. The story was published in the Humboldt Times along with a photo of Crew holding one of the casts. Locals had been calling the unseen track-maker "Big Foot" since the late summer, which Genzoli shortened to "Bigfoot" in his article. Bigfoot gained international attention when the story was picked up by the Associated Press. Following the death of Ray Wallace – a local logger – his family attributed the creation of the footprints to him. The wife of Scoop Beal, the editor of the Humboldt Standard, which later combined with the Humboldt Times, in which Genzoli's story had appeared, has stated that her husband was in on the hoax with Wallace.
1958 was a watershed year for not just the Bigfoot story itself but also the culture that surrounds it. The first Bigfoot hunters began following the discovery of footprints at Bluff Creek. Within a year, Tom Slick, who had funded searches for Yeti in the Himalayas earlier in the decade, organized searches for Bigfoot in the area around Bluff Creek.
As Bigfoot has become better known and a phenomenon in popular culture, sightings have spread throughout North America. In addition to the Pacific Northwest, the Great Lakes region and the Southeastern United States have had many reports of Bigfoot sightings.
Prominent reported sightings
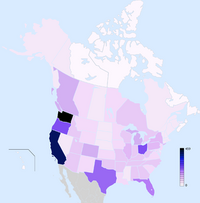
Distribution of reported Bigfoot sightings in Anglo-America.
About a third of all Bigfoot sightings are concentrated in the Pacific Northwest, with most of the remaining sightings spread throughout the rest of North America. Some Bigfoot advocates, such as cryptozoologist John Willison Green, have postulated that Bigfoot is a worldwide phenomenon. The most notable sightings include:
- 1924: Fred Beck claimed that he and four other miners were attacked one night in July 1924, by several "apemen" throwing rocks at their cabin in an area later called Ape Canyon, Washington. Beck claimed the miners shot and possibly killed at least one of the creatures, precipitating an attack on their cabin, during which the creatures bombarded the cabin with rocks and tried to break-in. The incident was widely reported at the time. Beck wrote a book about the event in 1967, in which he argued that the alleged creatures were mystical beings from another dimension, claiming that he had experienced psychic premonitions and visions his entire life of which the apemen were only one component. Speleologist William Halliday argued in 1983 that the story arose from an incident in which hikers from a nearby camp had thrown rocks into the canyon. There are also local rumors that pranksters harassed the men and planted faked footprints.
- 1941: Jeannie Chapman and her children claimed to have escaped their home when a large Sasquatch, allegedly 7.5 feet (2.3 m) tall, approached their residence in Ruby Creek, British Columbia.
- 1958: Bulldozer operator Jerry Crew took to a newspaper office a cast of one of the enormous footprints he and other workers had been seeing at an isolated work site at Bluff Creek, California. The crew was overseen by Wilbur L. Wallace, brother of Raymond L. Wallace. After Ray Wallace's death, his children came forward with a pair of 16-inch (41 cm) wooden feet, which they claimed their father had used to fake the Bigfoot tracks in 1958. Wallace is poorly regarded by many Bigfoot proponents. John Napier wrote, "I do not feel impressed with Mr. Wallace's story" regarding having over 15,000 feet (4,600 m) of film showing Bigfoot.
- 1967: Roger Patterson and Robert Gimlin reported that on October 20 they had captured a purported Sasquatch on film at Bluff Creek, California. This came to be known as the Patterson-Gimlin film, which is purported to be the best evidence of Bigfoot by many advocates. Many years later, Bob Heironimus, an acquaintance of Patterson's, claimed that he had worn an ape costume for the making of the film.
- 2007: On September 16, 2007, hunter Rick Jacobs captured an image of a possible sasquatch using an automatically triggered camera attached to a tree, prompting a spokesperson for the Pennsylvania Game Commission to say that it was likely an image of "a bear with a severe case of mange." Australian scientist and journalist Vanessa Woods wrote in "Scientriffic", a bimonthly magazine for ages 7+, that her Duke University colleague's informal measurements showed that the proportions of the creature were not similar to a bear's, although they could not discount the possibility that it was a hoax. The sighting happened near the town of Ridgway, Pennsylvania, in the Allegheny National Forest.
Appearances in Popular Media
Depictions of Bigfoot in popular media have been extremely varied, as it has been featured in comedy, fantasy and horror, and may be portrayed as anything, from savage near-human to supernatural beast; from man-sized to almost daikaiju-sized; from murderous brute to gentle giant. It is also relatively common for it to be mistakenly referred to as "Abominable Snowman" or even "Yeti" - names that should be reserved for the unrelated creature from the Himalayas.
In a particularly interesting occurrence, in the sci-fi series The Invisible Man (2000 – 2002) the chemical substance which grants the main character the ability to become invisible is produced by a gland taken from a sasquatch corpse, explaining that the creature has invisibility as a natural skill, which accounts for how it has managed to evade scientific detection for so long.
In Brett Davis' fantasy novel The Faery Convention, Bigfoots and Sasquatches appear among the several sapient races of "supernaturals" which have been living in the woodlands, hiding themselves from humanity. The terms "Bigfoot" and "Sasquatch" are not synonymous in this case, as the two are noted as being related but not quite the same.
In the animated series The Real Ghostbusters, Bigfoot is a being native to another dimension which escaped to our own world by entering a time warp.
Other works featuring Sasquatches or creatures closely similar, and/or identified as such, include:
- Abominable (2006)
- Back at the Barnyard, episodes "Otis Vs. Bigfoot" (2008) and "Mission: Save Bigfoot" (2010)
- Bigfoot (1970)
- Bigfoot (1987)
- Bigfoot (2006)
- Bigfoot (2012)
- The Capture of Bigfoot (1979)
- Clawed: The Legend of Sasquatch (2005), a.k.a. The Unknown
- Devil on the Mountain (2006), a.k.a. Sasquatch Mountain
- Garfield and Friends, episode "Bigfeetz" (1993)
- A Goofy Movie (1995)
- Harry and the Hendersons (1987)
- Hotel Transylvania (2012), cameo
- The Legend of Sasquatch (2006)
- Letters from the Big Man (2011)
- Night of the Demon (1980)
- Sanctuary (2008 – 2011)
- Sasquatch (2002), a.k.a. The Untold
- Sasquatch Hunters (2005)
- Snowbeast (1977)
- Snowbeast (2011)
- They Call him Sasquatch (2003)
- Teenage Mutant Ninja Turtles, episode "A Foot Too Big" (2014)
- Timon & Pumbaa, episode "Bigfoot, Littlebrain" (1999)



















